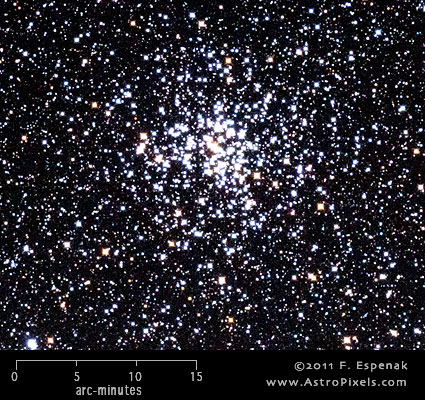
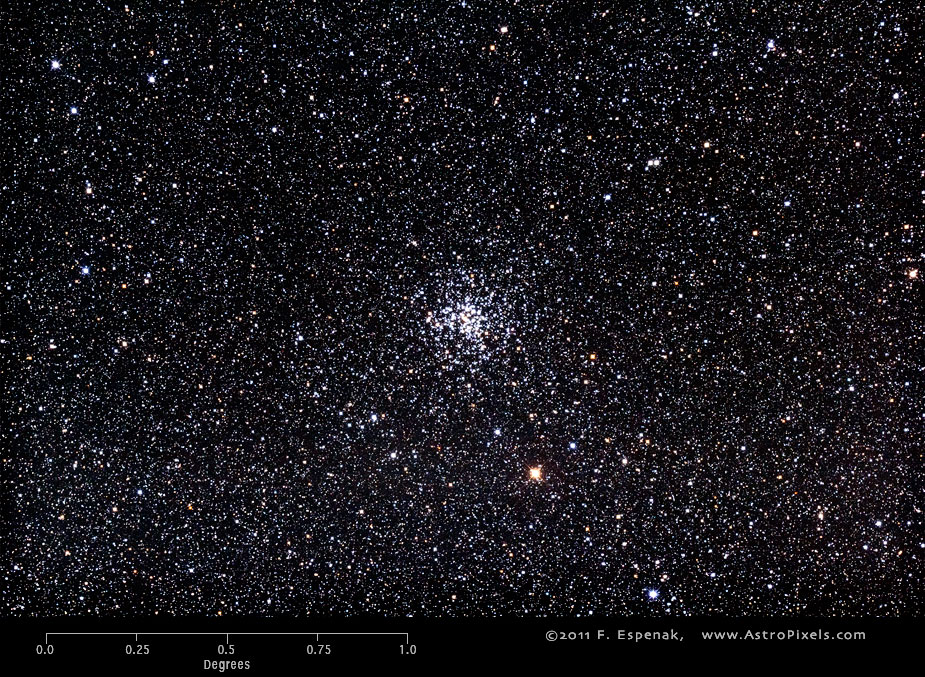
M37
Messier 37 or M37 (also designated NGC 2099) is an open cluster in the constellation Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.2 and its angular diameter is 24 arc-minutes. M37 lies at an estimated distance of 4400 light years. The Equinox 2000 coordinates are RA= 5h 52.4m, Dec= +32° 33´ which makes M37 best seen during the winter. The Messier Winter Star Chart shows the position of all Messier objects visible during that season.
The image above shows the uncropped view of M37 through the Takahashi E-180 Astrograph (North is up). The bright star 30 arc-minutes southwest of M36 is HR 2018 (magnitude 6.28). A 2x enlargement of this image appears to the right.
In spite of its inclusion in the Messier Catalog, this open cluster was actually discovered by G. B. Hodierna in 1654. Along with M36 and M38, it forms a trio of open clusters in Auriga. According to Kharchenko et al. (2005), the distance of M37 is 4510 light years and its diameter is 33 light years. It contains 2000 stars and its estimated age is 500 million years.
For more information, see the Messier Catalog as well as specific entries for M37 in Wikipedia and SEDS.
Messier's Description of M37
September 2, 1764
`Cluster of small stars, little remote from the preceding [M36], above the parallel of chi Aurigae; the stars are smaller, more close together and enclosing some nebulosity; with an simple refractor of 3.5 feet, one has pain to see the stars: this cluster is reported on the Chart of the second Comet of 1771, Mem. Acad. 1777.' (diam. 9')
Technical Details
- Object: M37
- Other Names: NGC 2099
- Object Type: open cluster
- Object Data: Apparent Magnitude = 6.2, Angular Size = 24 arc-minutes
- Object Position (Equinox 2000): RA= 5h 52.4m, Dec= +32° 33´, Constellation = Auriga
- Date/Time: 2011 Mar 27 at 03:27 UTC
- Location: Bifrost Astronomical Observatory, Portal, AZ
- Mount: Astro-Physics 1200GTO
- Telescope: Takahashi Epsilon 180 Hyperbolic Astrograph
- Camera: Canon EOS 550D (Rebel T2i) (modified with a Baader UV/IR filter)
- Field of View: 1.70° x 2.56° at 1.7 arc-sec/pixel (web version: 10.0 arc-sec/pixel)
- Exposure: 2 x 300s, f/2.8, ISO 800
- File Name: M37-01w.jpg
- Processing (Adobe Camera Raw): Graduated Filter, Vignetting Correction, Noise Reduction, White Balance, Curves
- Processing (Photoshop CS5): Average Images, Curves, Noise Reduction
- Original Image Size: 3454 × 5179 pixels (17.9 MP); 11.5" x 17.3" @ 300 dpi
- Rights: Copyright 2011 by Fred Espenak. All Rights Reserved. See: Image Licensing.