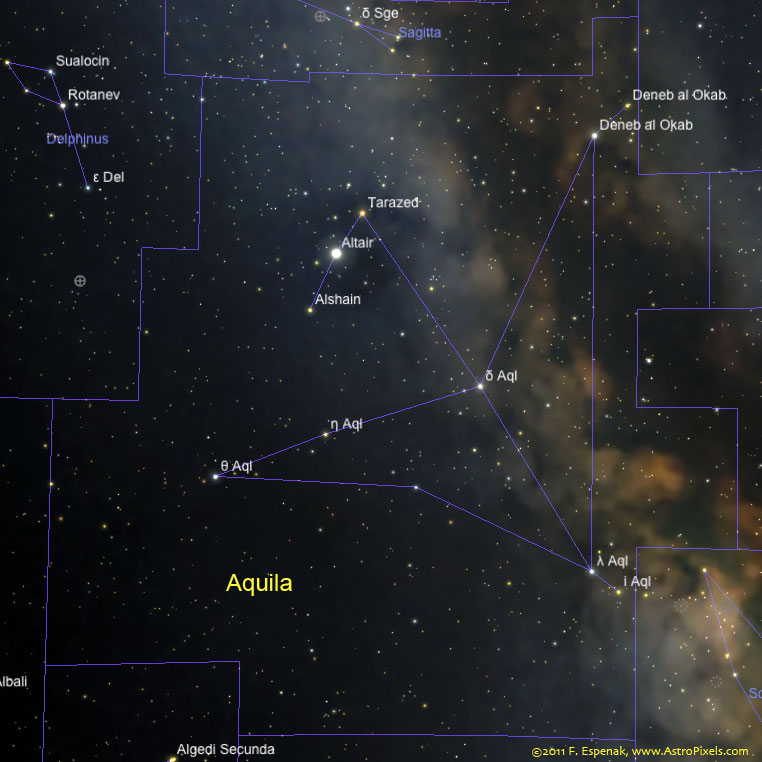
Aquila
Aquila is a Equatorial constellation otherwise known as the Eagle. It is one of the 48 Greek constellations originally described by the 2nd century astronomer Claudius Ptolemy (Wikipedia). Aquila remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (Wikipedia).
Aquila (abbrev. = Aql; genitive = Aquilae) covers 652 square degrees or 1.58% of the celestial sphere making it the 22nd largest constellation. It contains 124 stars brighter than apparent magnitude 6.5, the brightest star being Altair (Alpha Aquilae). See Aquila for a photo this constellation from Bifrost Observatory.
For more information see the entries for Aquila at Wikipedia and U. Wisconsin. For a chart of Aquila, see Aql (IAU).